Operating principle
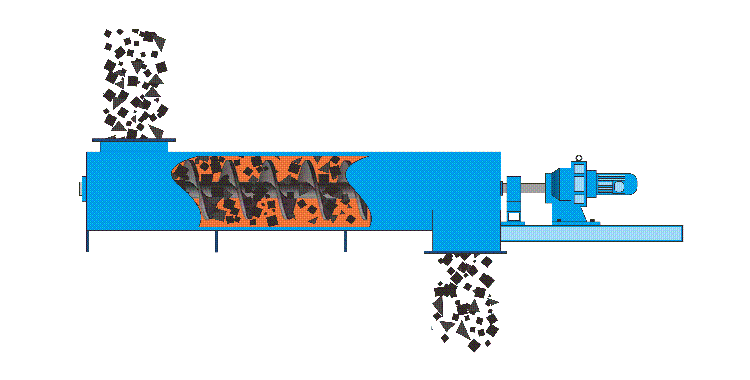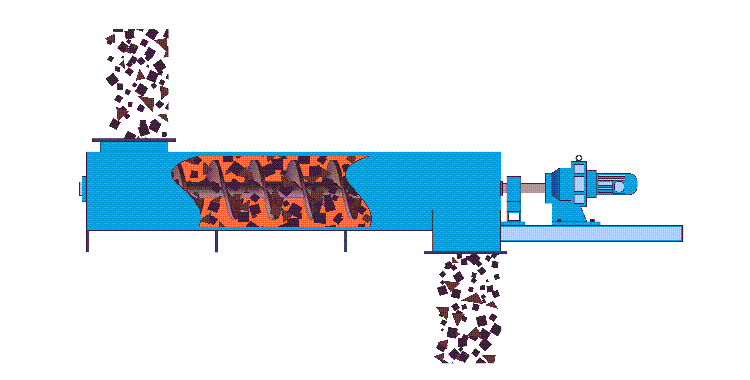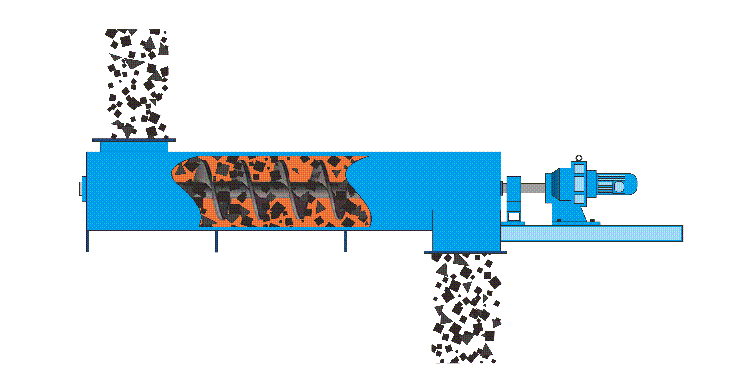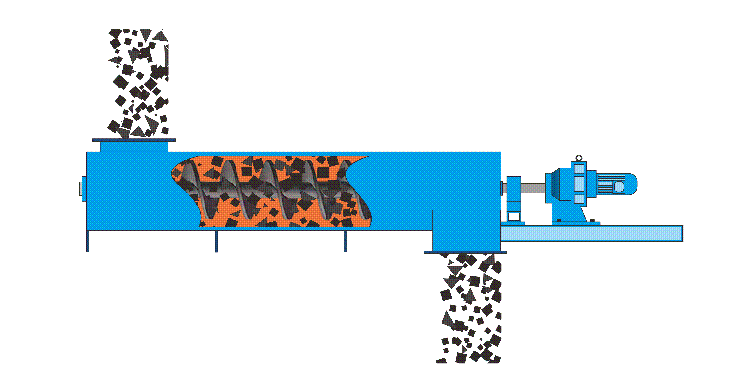
Material Transport Mechanism
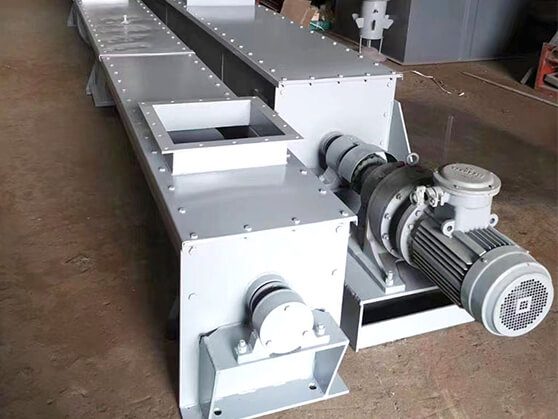
The U-type screw conveyor is meticulously designed to facilitate the efficient conveyance of diverse materials. Materials are introduced into the screw conveyor tube through an inlet that has been strategically positioned to optimize material flow and mitigate potential blockages.
Kinematic Transfer
Upon initiation, the motor engages a transmission mechanism that rotates the central shaft at a calibrated speed. This rotation activates the spiral blade, which is engineered with precise geometry to effectively propel materials along the length of the tube. The design ensures that even cohesive or granular substances can be transported with minimal degradation.
Conveying Orientation
The U-type screw conveyor exhibits operational versatility. It can transport materials either horizontally or at an incline based on specific operational requirements. Depending on its configuration and angle, it can elevate materials for height adjustments or lower them when gravitational assistance is advantageous. This adaptability renders it suitable for various industrial applications where spatial constraints may limit alternative conveying solutions.
Material Discharge System
As materials traverse through the system and reach designated discharge points within the pipeline, they are expelled through an outlet specifically designed for optimal flow management. This discharge mechanism may incorporate features such as gates or chutes that ensure smooth release while preventing spillage or backflow.
Critical Considerations
It is imperative to acknowledge that several factors influence both efficiency and capacity in this type of conveying system. These include specifications related to pipe diameter and screw flighting dimensions, pitch measurements between flights, rotational speed settings of the spiral blade, as well as intrinsic characteristics of each conveyed material—such as moisture content and fluidity levels. Therefore, meticulous selection and precise engineering considerations regarding these parameters are essential for achieving optimal performance across varied operational environments.
What are the advantages of U-shaped screw conveyors?
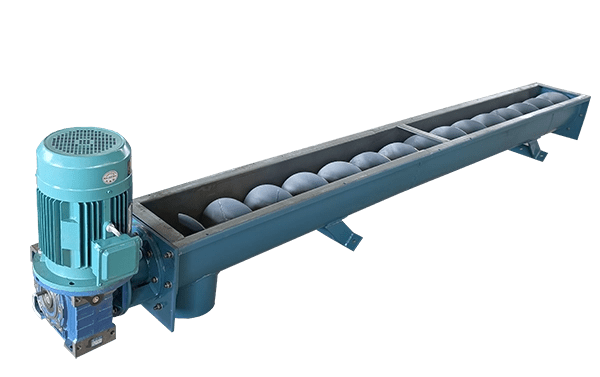
Functionally and in terms of conveying capacity, U-shaped screw conveyors are similar to tube screw conveyor. However, they offer easier operation due to their design.
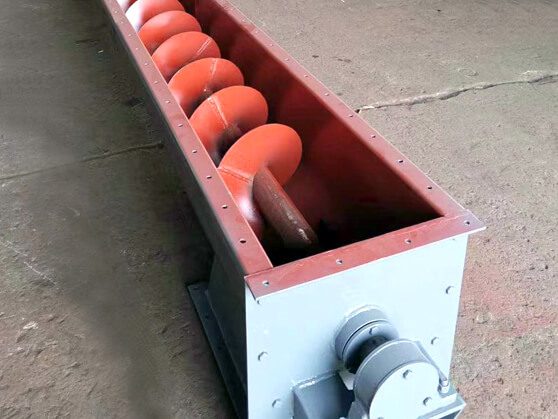
U-shaped screw conveyors provide a unique structural advantage that enhances their operational efficiency. Their open or fully enclosed design not only facilitates easier cleaning but also allows for straightforward inspection for blockages. This is particularly important in industries where hygiene and cleanliness are paramount, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Easier cleaning and blockage inspection
The ability to access the interior components without significant disassembly makes it simpler for operators to maintain optimal performance levels. By reducing dust pollution through effective sealing options, these systems contribute positively to workplace safety and environmental standards.
Convenient maintenance
With easy access for inspections, any failures in a U-shaped screw conveyor can be promptly addressed, unlike with tube screw conveyors. Regular maintenance checks can be performed more efficiently due to this accessibility, which minimizes downtime and ensures continuous operation.
Good thermal insulation without a cooling device
The open design allows for effective heat dissipation during mechanical blockages, eliminating the need for additional cooling systems. This feature is crucial in applications involving materials sensitive to temperature changes since it helps maintain product integrity while preventing overheating issues that could lead to equipment failure.
In addition to these benefits, U-shaped screw conveyors often have customizable configurations that allow them to fit into various layouts within production facilities seamlessly. They can handle different types of materials—ranging from bulk solids like grains and powders to semi-solid substances—making them versatile tools across multiple sectors including agriculture, mining, and manufacturing.
Applications
Agriculture and Food
Efficient material handling is essential in grain processing and storage. Conveyor systems facilitate the movement of grains, feed, seeds, and other agricultural products while minimizing loss. Automated sorting mechanisms enhance efficiency by categorizing materials based on size or quality.
Mining and Mineral Processing
The mining industry relies on conveyors to transport ores, coal, slag, sand, and stone over varying distances. These systems are designed to withstand harsh conditions while maintaining operational efficiency. Specialized designs may be used for specific materials to ensure safe transportation.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical
In chemical manufacturing and pharmaceuticals, precise material handling is crucial due to the nature of substances involved. Conveyors move powders like fertilizers or plastic granules safely through production stages while advanced monitoring technologies maintain product quality.
Water Treatment and Wastewater Treatment
Effective sludge management in water treatment facilities relies on conveyor systems that transport sludge from collection points to dewatering units efficiently. Compliance with hygiene regulations is critical since these systems handle potentially hazardous waste materials.
Building Materials
Reliable conveying solutions streamline the transportation of bulk building materials such as cement, mortar mixtures, gypsum powder, and aggregates across construction sites. This reduces manual labor requirements while ensuring consistent delivery rates.
Waste Management
In waste management operations—both municipal disposal and recycling—conveying technology facilitates efficient sorting and transportation of various waste streams including recyclables alongside general refuse. Automated belts can identify different materials for effective separation.
Food and Beverage
Within food processing plants where hygiene is paramount; conveyor systems designed for food-grade powders (like flour), granules (such as sugar), coffee beans play a key role in streamlining production lines while preventing cross-contamination during transit phases.



