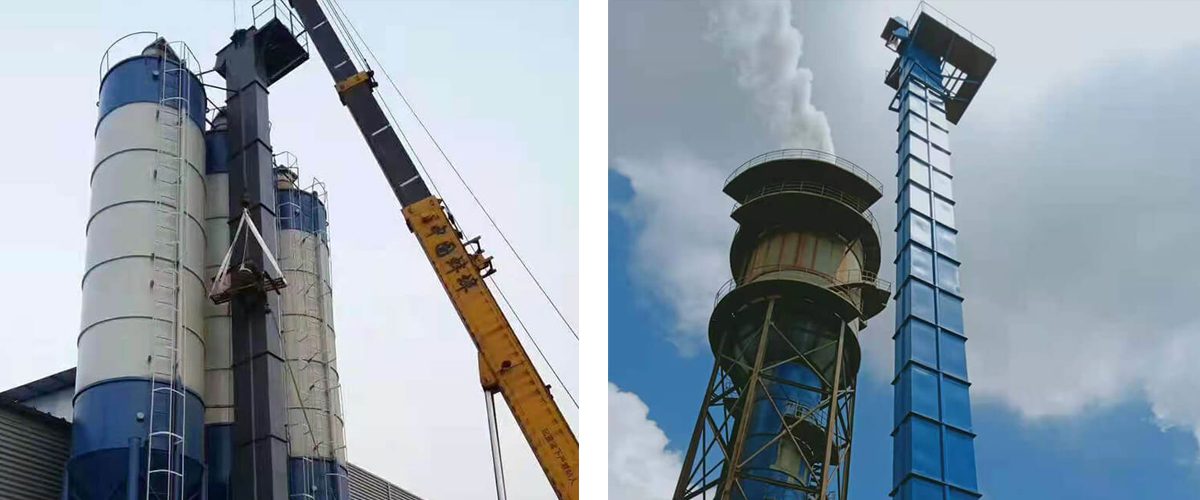
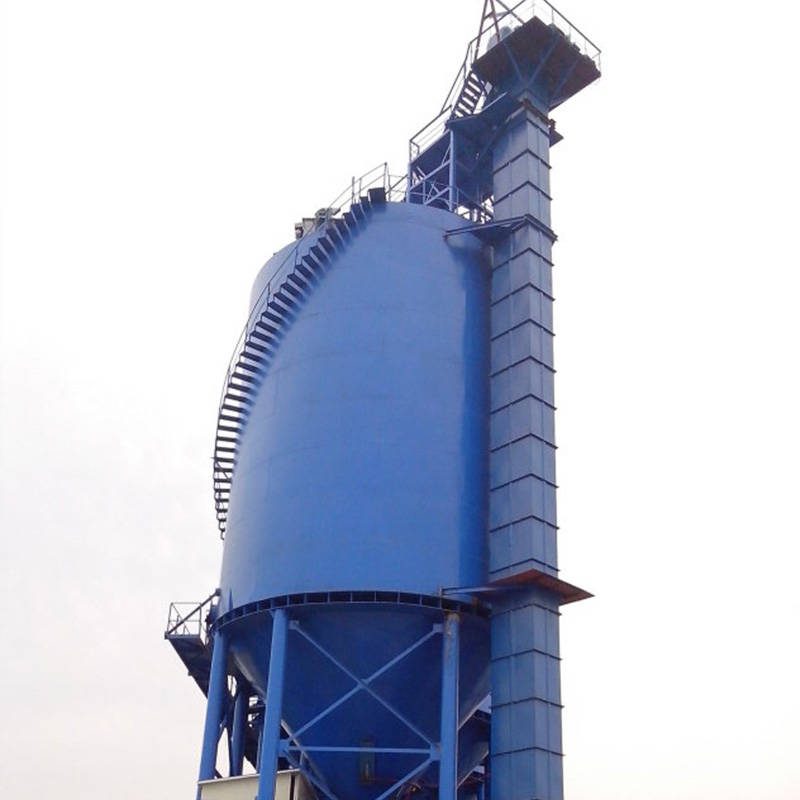
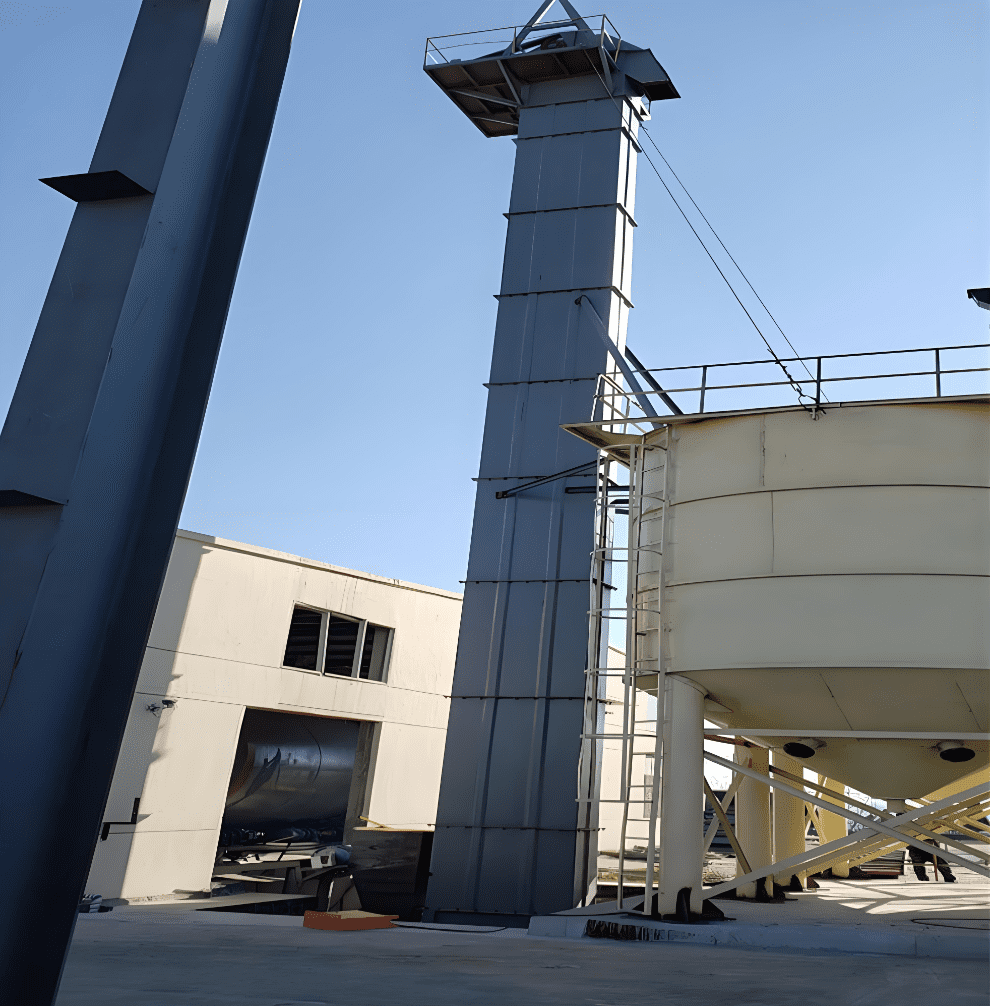
What Is a Bucket Elevator?
A bucket elevator is a continuous conveying machine that lifts materials vertically using a series of buckets evenly attached to an endless traction mechanism. The buckets are fixed to chains or belts and move materials upward in a vertical or near-vertical direction [1]. There are three types: ring chain, plate chain, and belt.
ダーコ provides professional bucket elevator solutions. We also produce explosion-proof bucket elevators compliant with the EU ATEX Directive. We ensure accurate selection and efficient conveying for your needs!
How a Bucket Elevator Works?
First, the buckets scoop material from the storage below. Then, the conveyor belt or chain lifts the buckets to the top. After passing over the top wheel, the buckets flip downward and discharge the material into the receiving chute.
Belt-driven bucket elevators use rubber belts mounted on drive pulleys (top or bottom) and redirecting pulleys.
Chain-driven bucket elevators use two parallel chains. Drive sprockets are at the top or bottom, and redirecting sprockets are at the opposite end.
Most bucket elevators have enclosures to prevent dust emissions.
Application: Moves materials from low to high positions. After loading via a vibrating table, the machine operates automatically for continuous upward transport.
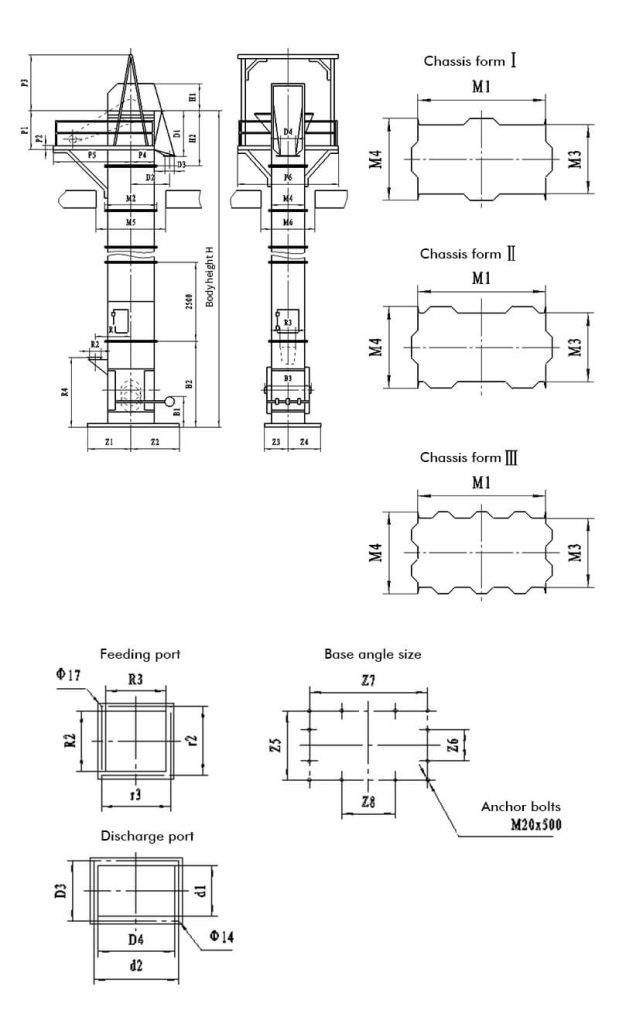
Main Components
A bucket elevator consists of:
Buckets
Drive unit
Top and bottom pulleys (or sprockets)
Belt (or traction chain)
Tensioning device
Enclosure.
1. Traction Components
(1) Rubber Belt
Attached with screws and elastic washers.
Belt width is 35–40 mm wider than the bucket.
Standard belts handle materials ≤60°C; heat-resistant belts handle ≤150°C.
(2) Chains
Single chain: Fixed to the back of buckets (for widths of 160–250 mm).
Double chain: Connects to both sides of buckets (for widths of 320–630 mm).
Disadvantage: Chain joints wear easily, requiring frequent maintenance.
(3) Sprockets
Drive sprockets engage with chains to transmit motion.
Tooth design ensures smooth movement and reduces impact.
Heat-treated for strength and wear resistance.
2. Bucket Types
(1) Deep Cylindrical Buckets
Tilted opening, large depth.
Used for dry, free-flowing granular materials.
(2) Shallow Buckets
Tilted opening, small depth.
Used for wet or sticky granular materials.
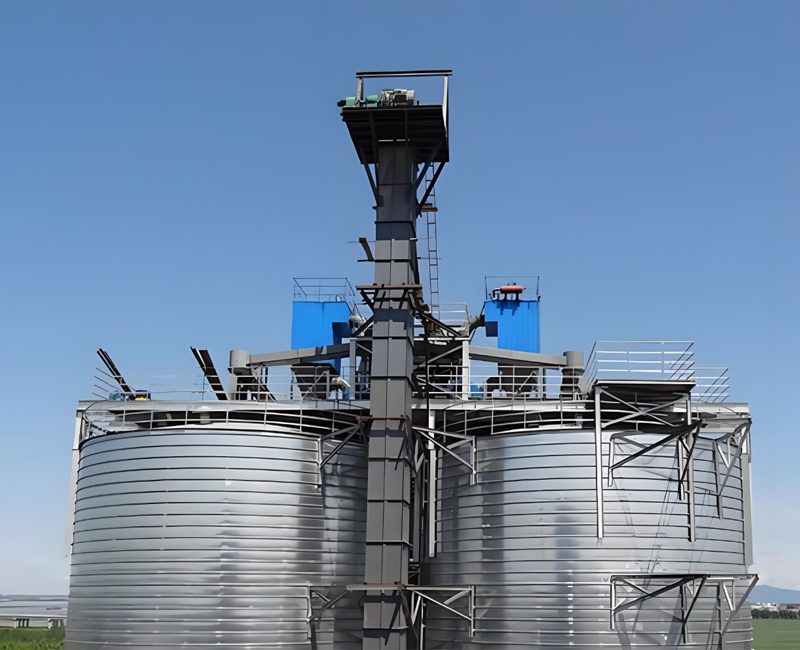

Key Features
Bucket elevators offer:
シンプルな構造
Low maintenance
High efficiency
Stable operation
Wide application range
利点がある:
Low power consumption: Flow-through feeding and induced discharge reduce wasted energy.
Broad material compatibility: Handles powders, small particles, and abrasive materials with minimal dust.
High reliability: Advanced design ensures over 20,000 hours of trouble-free operation.
Long lifespan: Gentle material handling reduces wear and collisions.
Common Types
Bucket elevators are classified by transmission structure :
1. TD Series
Models: TD100 (rare), TD160, TD250, TD315, TD400, TD500, TD630, TD800, TD1000.
Widely used for general purposes.
2. TH Series
Uses forged ring chains for high strength.
Ideal for powders, small particles, and heavy materials.
Higher capacity and efficiency than TD series.
3. NE Series (Plate Chain)
Replaces older TB series.
Named by capacity (e.g., NE150 = 150 tons/hour).
Subtypes: NSE and high-speed models.
4. TG Series (Reinforced Belt)
Uses steel-reinforced belts for heavy-duty lifting.
Common in grain handling (“grain-dedicated bucket elevator”).
5. Other Models
HL (ring chain), GTD, GTH (variants of above).
Selection Guide
1. Discharge Methods
Centrifugal discharge (high speed): For powders and small particles.
Gravity discharge (low speed): For large, abrasive materials (e.g., limestone).
2. Traction Component Comparison
| タイプ | Pros | Cons | Max Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chain | Durable, simple | Heavy | 250°C |
| Plate | Lightweight, strong | Joint wear | 250°C |
| ベルト | Simple | Not for abrasive materials | 60–120°C |
3. Selection Steps
素材タイプ (powder/granular/lumps).
Properties (moisture, stickiness).
Bulk density (>1.6 requires special calculations).
必要容量 → Choose model → Confirm bucket type → Finalize.
Bucket Rule:
Powders: Shallow/curved buckets (centrifugal discharge).
Lumps: Deep buckets (gravity discharge).
アプリケーション
外見の数字:
Need Help? 連絡先 ダーコ for expert advice! Our engineers provide customized solutions and after-sales support to ensure optimal performance.


